The Electrification Terminology Glossary

Here are all the definitions for the essential terminology to know in the electrified future.
Cars, being the technological masterpieces that they are becoming these days, are undoubtably complicated machines, with a lot of names, acronyms and terminology to navigate around.
To many a motorist who is just seeking a tool to get from A to B, terms that are commonly bounced around today in the world of cars like VVT-I and DOHC might as well be gibberish to them. Unfortunately however, these automotive jargon are soon to only get even more complicated, as the auto industry transitions towards the electrified future.

No longer does the automotive jargon only limit itself to the typical internal combustion engine terms that many might vaguely know what it means, like VTEC or DCT etc. With electrification on the horizon, there is soon to be a whole new set of words that will probably further puzzle the car buyer’s of the future.

Handily though, down below is a simplified guide of (nearly) all the EV terms that one needs to know, to help many a hapless motorist decode what the salesman will probably be talking about when walking into the showrooms during one’s next car purchase.

EV Classification Terminology
EV: Electric Vehicle
An umbrella term that classifies all types vehicles that are driven by an electric motor. Though these days, it is typically associated with battery electric vehicles (BEV).

BEV: Battery Electric Vehicle
An electric vehicle that is powered solely by the onboard battery pack. The most common type of fully electric vehicles to date.
Examples of BEVs include all models of the Tesla lineup, Polestar 2, Honda e, Nissan Leaf and many others.

FCEV: Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle
A fully electric vehicle that is powered by a hydrogen fuel cell. The main electrical source for the electric motor is generated from a chemical reaction between the compressed hydrogen stored in the onboard tank, and atmospheric oxygen.
Examples of FCEVs include the Toyota Mirai, Honda Clarity and Hyundai Nexo.

Hybrid Classification Terminology
Hybrid
A vehicle that features both a dedicated traction electric motor and a petrol/diesel internal-combustion engine. Both powertrain systems can independently send power to the driven wheels, or work as a combined unit to deliver additional power when required.
Each manufacturer would tend to give their hybrid systems its own specialised name, like Honda’s i-MMD system. Suffice to say however that, by and large, they all function on the same basic principle.
Examples of hybrid vehicles include the Toyota Prius, Honda Insight and the Hyundai Ioniq.

PHEV: Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
A hybrid vehicle that is capable of recharging its on-board batteries that feed the electric motor via an external power supply.
Currently the most common type of electrified vehicles sold in Malaysia. Typically features an external charging port on the front passenger-side fender.
Examples of PHEVs include the Volvo XC90 Recharge and the BMW 330e.

MHEV: Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Also known as battery-assisted hybrid vehicles (BAHV). A hybrid vehicle that typically utilises an integrated starter-generator (ISG) instead of a dedicated electric traction motor, along with a smaller battery pack.
Unlike a normal hybrid, the ISG rarely powers the driven wheels independently for an extended period of time. Instead, their main purpose is to improve the fuel efficiency of the internal-combustion engine by allowing for the engine to be turned off when coasting, braking, or stationary. These MHEVs usually run on a 48 V power supply.
Examples of MHEVs include the Nissan Serena S-Hybrid and the Lamborghini Sian.

REEV: Range Extended Electric Vehicle
A hybrid vehicle that is solely driven by the electric motor. The auxiliary internal combustion engine is used only to supplement battery charging.
Examples of REEVs include the BMW i3 Range Extender, Chevrolet Volt and Fisker Karma.

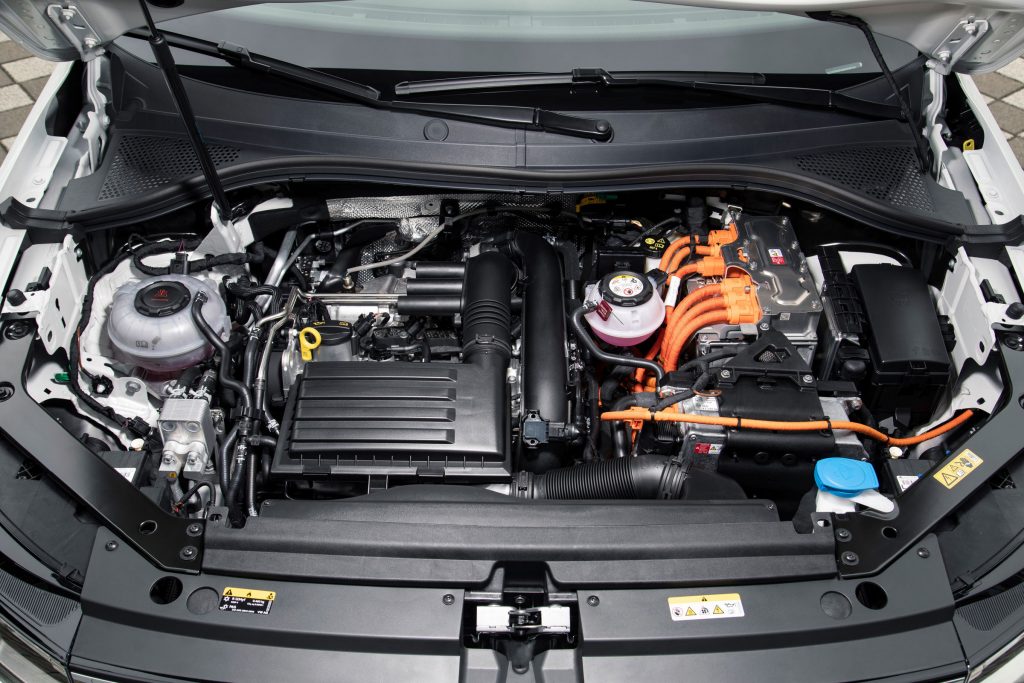
EV Component Terminology
Traction Motor/Permanent Synchronous Motor
Common terms to describe the electric motor within an EV which drives the wheels.
ISG: Integrated starter-generator
Essentially a simplified version of a traction motor that kicks in when an added boost of power is required. Its main purpose is actually to recuperate braking energy through regenerative braking.

EV Unit Terminology
kWh: kilowatt-hour
A unit which typically denotes the battery capacity of an EV. Could be thought of as the size of a fuel tank in a conventionally-powered vehicle.

kW: kilowatt
A unit which is most commonly used to denote engine power. Could be thought of as an equivalent to horsepower. Now however, it is also being used to quantify charging rates. The higher the kW number, the faster the rate of charge.





