Development of EV Charging Infrastructure in Singapore

Singapore’s automotive think tank is thinking ahead unlike its Malaysian counterparts who have been siting quiet with little effort to move electric vehicle (EV) adoption in Malaysia. With the global crisis of COVID-19, the Singapore Land Transport Authority is still working to bring higher EV adoption to the island nation. Here below is the LTA’s latest effort in EV adoption.
PRESS RELEASE: As part of the Government’s commitment to create a sustainable transport system, the Land Transport Authority (LTA) and the Energy Market Authority (EMA) jointly announced the addition of Japanese fast-charging method CHAdeMO as an optional public charging standard for electric vehicles (EVs). This enables charging providers to bring in a larger range of public charging options for EV users and supports the wider adoption of EVs in Singapore.
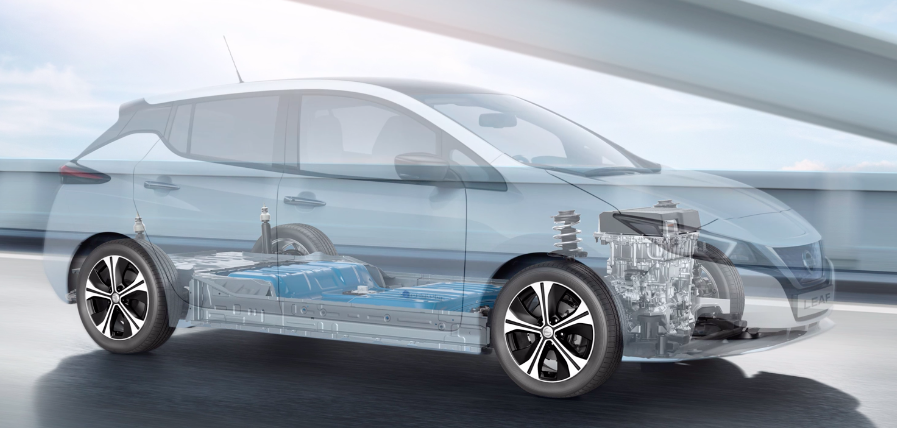
Adopted primarily by Japanese EV manufacturers, CHAdeMO (an abbreviation of CHArge de MOve) allows for fast charging of EVs using a Direct Current (DC) interface. A CHAdeMO DC charger with a power rating of up to 120 kilowatts (kW) can fully charge an electric car in about 30 minutes. Some examples of EV models equipped with CHAdeMO charging inlets include the Nissan Leaf, Mitsubishi iMiEV and Honda Fit EV.
Under the Technical Reference 25 (TR25), it is mandatory for charging service operators to provide Type 2 Alternating Current (AC) (slow charging) and/or Combo 2 (DC) (fast charging) chargers at their public charging stations. CHAdeMO will be added as an optional public charging standard and not as a national public charging standard under TR25. This means that it is not mandatory for charging service operators to provide CHAdeMO chargers at their public charging stations.
CHAdeMO DC chargers with a power rating of not more than 120kW can be imported and installed in Singapore, as long as they are provided alongside Type 2 AC and/or Combo 2 DC charging points. This is to ensure sufficient inter-operability for existing EVs in the market.
As the local EV ecosystem grows, the Government will continue to review Singapore’s EV charging regulations to ensure their relevance.
The national EV charging standard, Technical Reference 25 (TR25) was established in 2010 and revised in 2016 to specify the mandatory technical specifications and safety requirements for EV charging systems in Singapore. Under TR25, there are two national public charging standards: Type 2 (AC) (slow charging) and Combo 2 (DC) (fast charging).




